What is Autoimmune Disease? – Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, 10 Key Facts, UPSC Questions
Table of Contents
Introduction to Autoimmune Disease UPSC
Welcome to PreCrack! Recently, Due to CAR-t Cell therapy, the Auto Immune Disease or Autoimmune Disease was in News. There are numbers of celebrities has talked about these disease, mostly women. Now, knowing about Autoimmune Disease are crucial for us.
In India, If you are preparing for Major competitive examinations such as UPSC, SSC & more, then knowing about Autoimmune Disease lso help us to cover one more topic of UPSC Current Affairs. If you are also here to know about Autoimmune Disease in detail such as its current affairs, Autoimmune Disease symptoms, causes, types, diagnosis, treatment and best hospitals for Autoimmune Disease treatment in India, then this blog will going to help you all around.

Read Also | How Lethal is Kyasanur Forest Disease?
Why Auto Immune Disease in News? – UPSC Current Affairs 2024
Recently, Autoimmune Disease was in news due to CAR T-cell therapy. It was in the news recently due to its potential to treat autoimmune diseases.
A study published in December 2023 showed that CAR T-cell therapy led to complete remission in 15 patients with severe autoimmune diseases, including lupus, myositis, and scleroderma. The patients had been previously treated with standard therapies but had not responded well. After receiving CAR T-cell therapy, all of the patients went into remission and were able to stop taking their medications.
This is a very promising development for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. CAR T-cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy that involves engineering a patient’s own immune cells to attack cancer cells. In this case, the CAR T-cells were engineered to target B cells, which are immune cells that play a role in many autoimmune diseases.
The study is small, and more research is needed to confirm these results.
Source – Nature.com
What is Auto Immune Disease? – Auto Immune Disease UPSC
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s defense system, the immune system, mistakenly attacks its own cells, tissues, and organs, thinking they are threats. Normally, the immune system protects these components o our body against harmful invaders like viruses and bacteria, but in autoimmune conditions, it turns against the body itself. Generally it happens due to overactive Immune System.
This self-attack can lead to inflammation, pain, and damage to various parts of the body. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and type 1 diabetes are examples of autoimmune diseases. The exact causes are not fully understood, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to contribute to their development.
What is CAR-T Cell Therapy?
CAR-T cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy used to treat some aggressive cancers. It stands for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell Therapy. Here’s how it works:
1. Extracting and engineering T cells
- T cells, a type of white blood cell important for fighting infections, are extracted from the patient’s blood.
- In a lab, these T cells are genetically modified by adding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) to their surface. This receptor helps them recognize and target specific proteins on cancer cells.
2. Expanding the modified T cells
The engineered T cells, now called CAR-T cells, are grown in the lab under special conditions to increase their number.
3. Reinfusing the CAR-T cells
The multiplied CAR-T cells are infused back into the patient’s bloodstream through an intravenous line.
4. Attacking cancer cells
Once returned to the body, the CAR-T cells recognize and attack the cancer cells with the specific protein they were designed to target.
Key points about CAR-T cell therapy
- It’s a personalized treatment, as the CAR is designed to target a specific protein on the patient’s cancer cells.
- It’s a powerful therapy, but it can also have serious side effects like cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity.
- It’s currently approved for several types of blood cancers, and research is ongoing for expanding its applications.
Key Facts about CAR-T cell therapy
| Key Facts | Details |
| Definition | A type of immunotherapy that uses genetically modified T cells to target and destroy cancer cells. |
| Invented | 1989 |
| Inventor | Dr. Zelig Eshhar |
| Uses | Treatment of certain aggressive cancers, including leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. |
| Success rate | Varies depending on the type of cancer and other factors, but can be very high for some cancers. |
| How it works | T cells are extracted from the patient, genetically modified to recognize specific proteins on cancer cells, expanded in number, and then infused back into the patient to attack the cancer cells. |
Why CAR-T Cell Therapy was in the news in India?
The main reason CAR-T therapy made headlines in India is due to the development and commercialization of the country’s first indigenous therapy, NexCAR19:
- First successful case: In October 2023, a 64-year-old patient became the first in India to be declared cancer-free after receiving NexCAR19 treatment. This marked a significant milestone for accessibility and affordability of this advanced therapy.
- Cost-effectiveness: The Indian treatment costs significantly less compared to similar therapies abroad. Dr. Gupta, the first patient, paid $50,000 compared to the usual $480,000 for overseas options.
- Wider availability: Initially approved for B-cell cancers like leukemia and lymphoma, NexCAR19 is now available in over 30 hospitals across 10 Indian cities.
- Future potential: The success of NexCAR19 paves the way for further research and development of CAR-T therapies for broader applications in cancer treatment.
Source – India Today
About NexCAR19 Treatment
We have added a comprehensive details about NexCAR19 Treatment below-
What is it?
NexCAR19 is a CAR-T cell therapy designed to treat specific types of blood cancers. It involves extracting a patient’s T cells, modifying them to target cancer cells, and then reinfusing them back into the patient to attack the cancer.
What Cancers Does it Treat?
Currently approved for B-cell lymphomas and B-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia where other treatments have failed.
How Does it Work?
NexCAR19 targets a protein called CD19, found on many B-cell cancer cells. The modified T cells recognize and eliminate these cancer cells.
Key Benefits:
- India’s first indigenous CAR-T therapy: More accessible and affordable for patients compared to foreign options.
- High Success Rate: Promising results observed in early trials and clinical use.
- Cost-Effective: Significantly cheaper than similar therapies abroad.
- Available in India: Increasingly accessible across various hospitals.
Important Facts:
- Still under development and research for broader applications.
- May come with potential side effects like cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity.
- Not suitable for all patients and requires specific criteria.
Further Resources:
ImmunoACT NexCAR19 page: https://www.immunoact.com/nexcar19
What are Causes of Autoimmune Disease?
the exact cause of Autoimmune Diseases (AID) is still unknown. Researchers are actively investigating, but there are several theories and risk factors associated with their development:
Risk factors:-
- Genetics: Having a family member with an AID increases your risk, but it’s not deterministic. Specific genes might make you more susceptible.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain viruses, bacteria, toxins, or chemicals might trigger AID development in individuals with genetic predisposition.
- Medications: Certain drugs can induce changes in the body that confuse the immune system. Statins, antibiotics, and blood pressure medications, in particular, may have such effects.
- Age and sex: AID usually presents in young to middle adulthood, and women are more affected than men.
- Diet and gut microbiome: Imbalances in gut bacteria have been linked to some AIDs, but the exact role is still under investigation.
- Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of developing certain AIDs.
Potential triggers:-
- Infections: Some microorganisms might mimic healthy tissues, confusing the immune system and leading to an attack.
- Medications: Certain medications can rarely trigger an autoimmune response.
- Obesity
- Hormonal changes: Shifts in hormone levels, like during puberty or pregnancy, might contribute.
Source – WebMD.com
Symptoms of Auto Immune Disease
Autoimmune diseases (AIDs) manifest differently depending on the specific body systems they affect. However, some common symptoms can occur across a range of AIDs:
General:-
- Fatigue: Feeling persistently tired and lacking energy.
- Fever: Low-grade fever that may come and go.
- Pain: Joint pain, muscle aches, or general discomfort.
- Swelling: Inflammation in joints, tissues, or organs.
- Skin problems: Rashes, itching, hair loss, or sensitivity to sunlight.
- Digestive issues: Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, or constipation.
- Neurological problems: Headaches, memory problems, mood changes, or difficulty concentrating.
Points to Consider:-
- These are just common symptoms, and individual experiences can vary significantly.
- Some AIDs have specific, distinctive symptoms beyond these general ones.
- The presence of some of these symptoms doesn’t necessarily indicate an AID; they can occur in other conditions as well.
Types of Autoimmune Disease
Autoimmune diseases (AIDs) are a diverse group of conditions where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues. Over 80 different types of AIDs exist, each affecting different parts of the body and presenting with varying symptoms. Here’s a glimpse into some of the most common types:
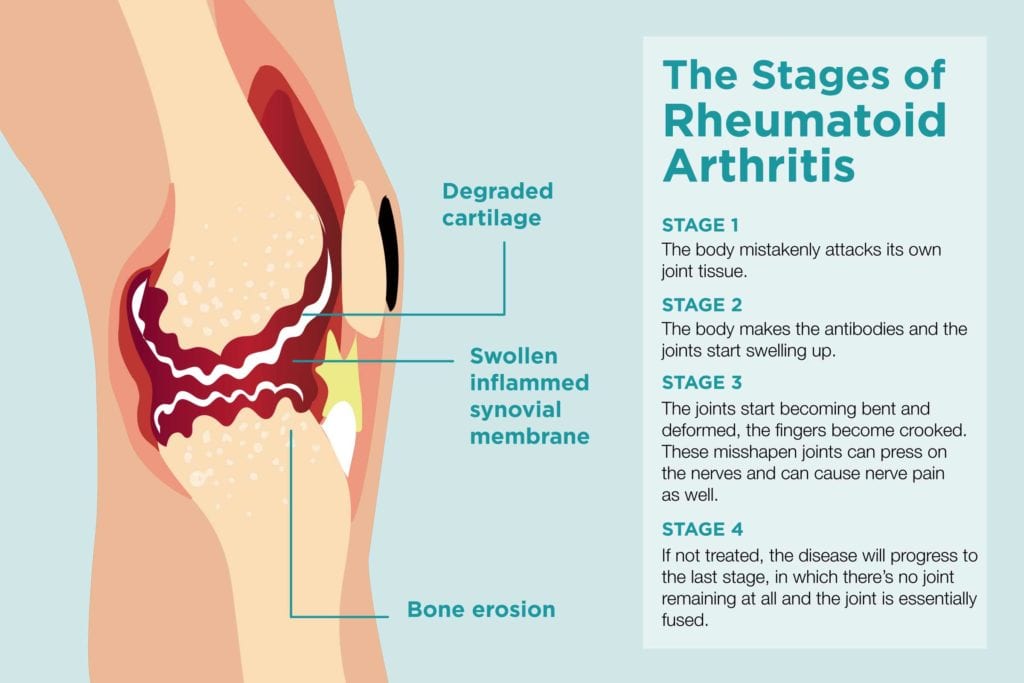
1. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
This chronic inflammatory disease primarily targets the joints, causing pain, stiffness, swelling, and eventual damage.
2. Lupus
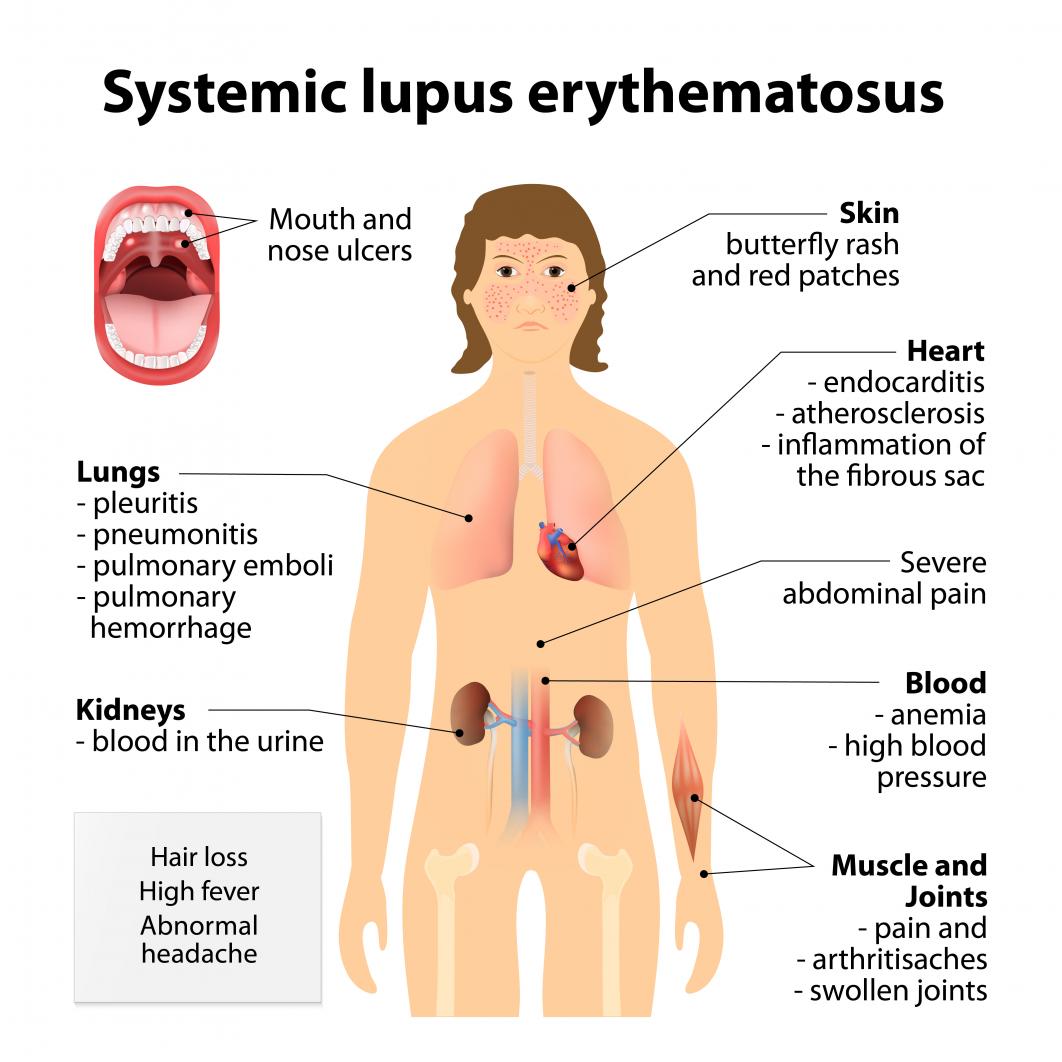
An autoimmune disease that can affect multiple organs and tissues, leading to a wide range of symptoms like fatigue, skin rashes, joint pain, and organ inflammation.
3. Psoriasis
A chronic skin condition characterized by thick, red, scaly patches that can appear anywhere on the body.
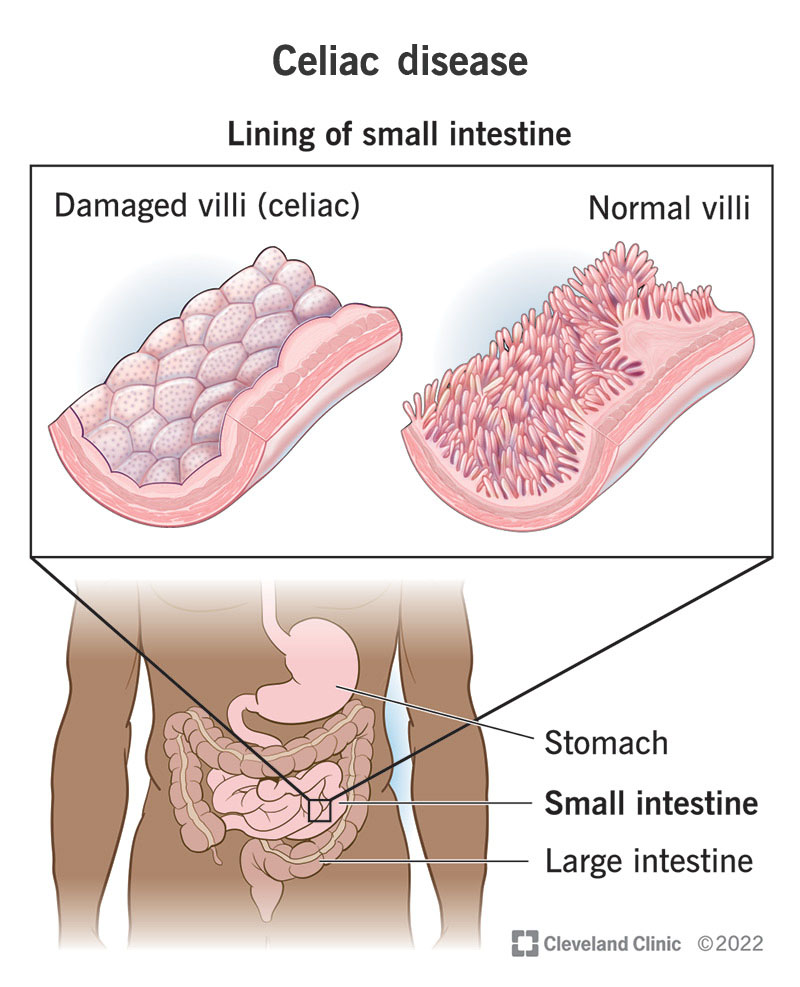
4. Celiac Disease
An autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. It damages the small intestine and leads to digestive problems like bloating, diarrhea, and weight loss.
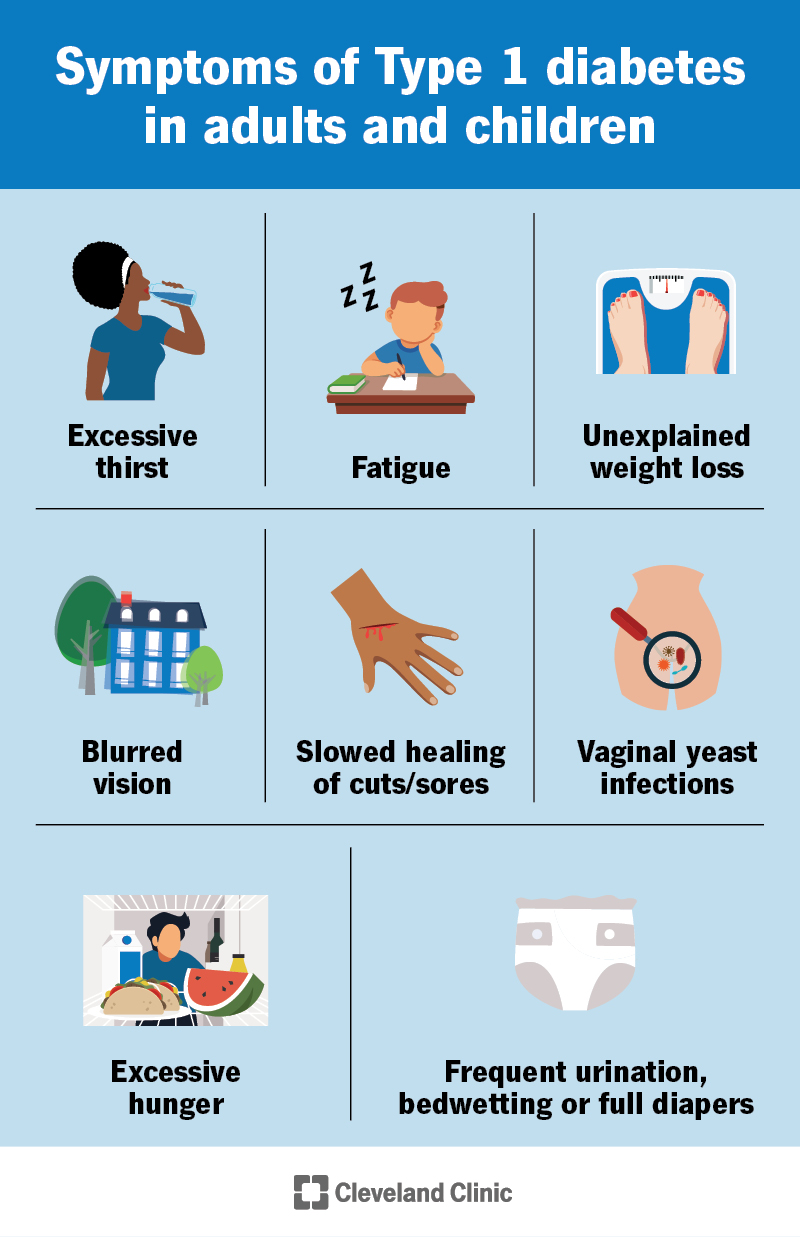
5. Type 1 Diabetes
An autoimmune condition where the body destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to high blood sugar levels and requiring insulin injections for management.
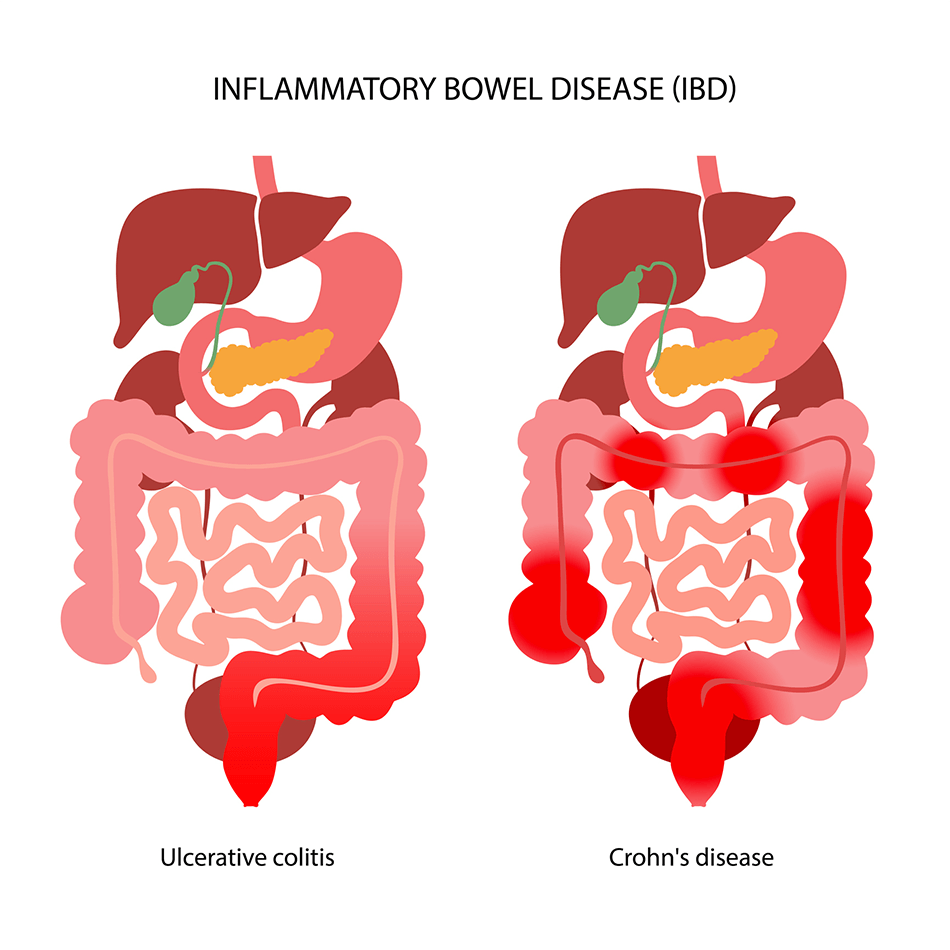
6. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
This group of chronic inflammatory conditions includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, affecting the digestive tract and causing symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and bleeding.
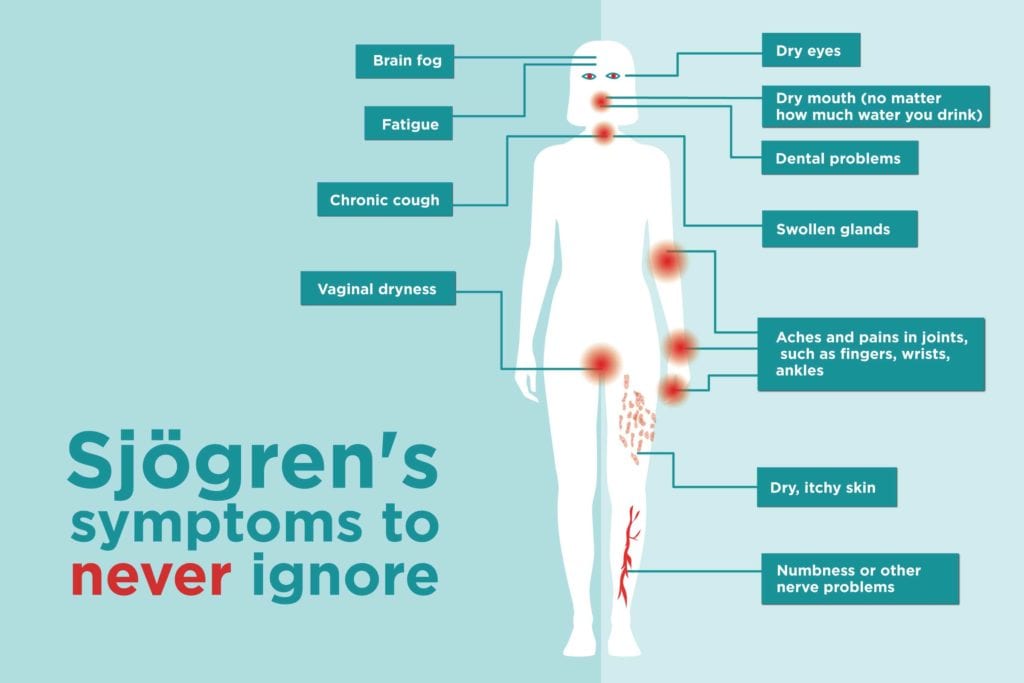
7. Sjögren’s Syndrome
An autoimmune disorder that attacks the glands responsible for producing tears and saliva, leading to dryness in the eyes and mouth.
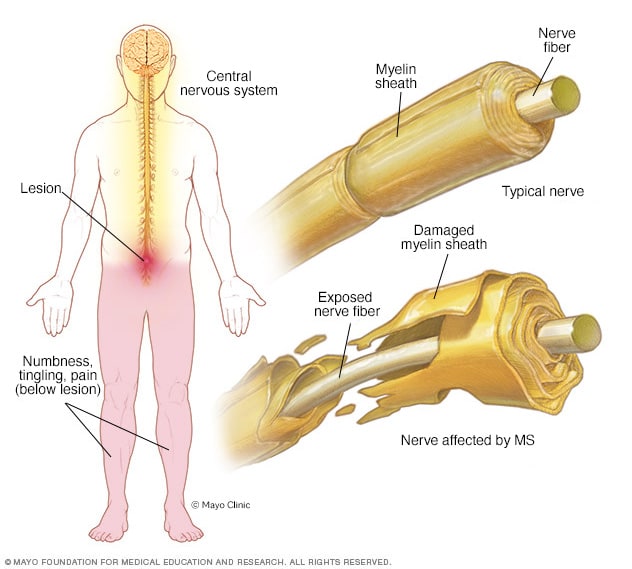
8. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
An autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, causing damage to the myelin sheath protecting nerve fibers and leading to various neurological symptoms like muscle weakness, vision problems, and coordination difficulties.
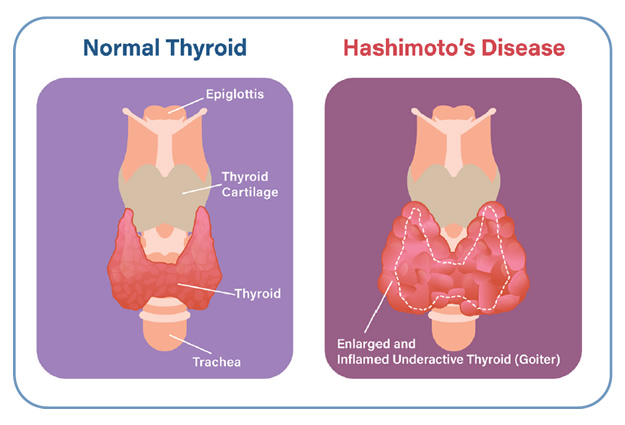
9. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
An autoimmune condition that attacks the thyroid gland, leading to underproduction of thyroid hormones and causing symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold.
10. Graves’ Disease
An autoimmune disorder that causes the thyroid gland to overproduce thyroid hormones, leading to symptoms like anxiety, heart palpitations, and weight loss.
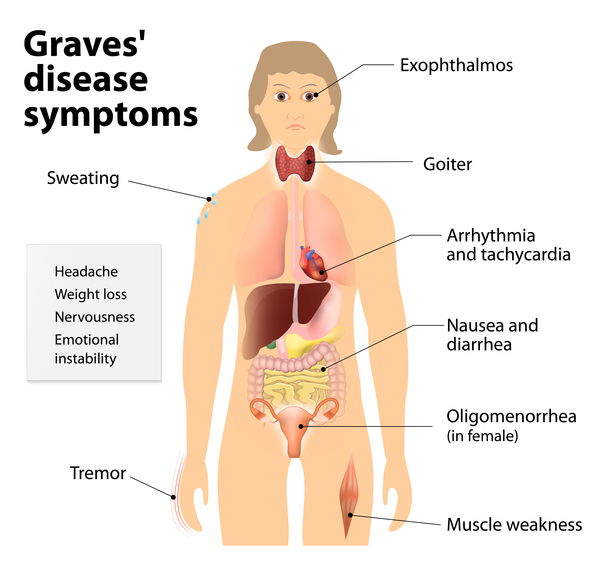
Remember, this is not an exhaustive list, and many other types of AIDs exist. If you experience any concerning symptoms, consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis of Auto Immune Diseases
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases can be complex due to the diverse variety and often overlapping symptoms. However, several steps are involved to reach an accurate diagnosis:
1. Detailed Medical History:
- Your doctor will take a thorough history of your symptoms, including their onset, duration, severity, and any trigger factors.
- They’ll also inquire about your family history of autoimmune diseases and review your current medications and lifestyle habits.
2. Physical Examination:
This may involve assessing for signs of inflammation, swelling, tenderness, or other physical features related to specific AIDs.
3. Laboratory Tests:
- Blood tests: Various blood tests can be done, including complete blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), antinuclear antibody (ANA) test, and specific autoantibody tests targeting individual AIDs.
- Other tests: Depending on suspected AID, additional tests like X-rays, imaging studies, biopsies, or tissue assessments might be employed.
4. Diagnostic Criteria:
Each AID has specific diagnostic criteria defined by medical societies. Combining clinical findings, laboratory results, and meeting these criteria guides the diagnosis.
5. Specialist Consultation:
In some cases, referral to a rheumatologist, dermatologist, neurologist, or other specialist familiar with specific AIDs might be necessary for further evaluation and diagnosis.
Treatment of Auto Immune Diseases
Unfortunately, there is no single cure for Autoimmune Diseases (AIDs) as they involve the complex interaction of various factors. However, various treatment options focus on managing symptoms, reducing inflammation, and preventing tissue damage. These treatments address both the general aspects of AID and the specific features of each individual disease. Here’s an overview:
Medications
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Reduce inflammation and pain, like corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Immunosuppressants: Suppress the immune system’s activity to prevent further attacks on healthy tissues, like methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, and biologics.
- Specific medications: Certain AIDs have targeted medications, like insulin for type 1 diabetes or thyroid hormone replacement for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- Physical therapy: May help manage pain, improve joint function, and maintain mobility in affected areas.
- Occupational therapy: Helps individuals adapt to physical limitations and maintain daily activities.
Lifestyle modifications
- Diet: Certain dietary changes might benefit specific AIDs. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve overall health and manage symptoms.
- Stress management: Techniques like yoga or meditation can help cope with stress, which can exacerbate AID symptoms.
Best Hospitals in India for Treatment of Auto Immune Diseases
There are several Indian institutions are consistently achieving the recognition for their expertise in treating autoimmune diseases. Here are some renowned options:
1. All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi
Recognized for its advanced research and treatment facilities, AIIMS Delhi boasts a dedicated Department of Rheumatology, Immunology & Allergy, offering comprehensive care for various autoimmune conditions.

2. Medanta – The Medicity, Gurgaon
This multispecialty hospital houses a Center for Rheumatic Diseases, offering specialized diagnosis, treatment, and clinical trials for diverse autoimmune disorders.

3. Sir H. N. Reliance Foundation Hospital & Research Centre, Mumbai
Renowned for its advanced medical technologies and patient-centric approach, this hospital’s Department of Rheumatology, Allergy & Clinical Immunology provides comprehensive care for autoimmune conditions.

4. Jaslok Hospital & Research Centre, Mumbai
Established in 1971, Jaslok offers specialized Rheumatology and Immunology services, including advanced diagnostics and targeted treatment plans for various autoimmune diseases.

5. Sri Shankaradeva Children’s Hospital, Bangalore
Primarily focusing on pediatric care, this hospital has a dedicated Rheumatology department well-equipped to manage different childhood autoimmune disorders.
6. Apollo Hospitals, Chennai
With a strong presence across India, Apollo Hospitals Chennai’s Department of Rheumatology & Immunology offers advanced treatment options, including biologics and clinical trials, for various autoimmune conditions.

7. Amri Hospitals, Kolkata hospital
Medica Superspecialty Hospital, Kolkata: Established in 2008, Medica’s Department of Rheumatology & Immunology delivers comprehensive care for a wide range of autoimmune disorders, utilizing advanced diagnostic tools and evidence-based treatment approaches.

8. Medica Superspecialty Hospital, Kolkata
Established in 2008, Medica’s Department of Rheumatology & Immunology delivers comprehensive care for a wide range of autoimmune disorders, utilizing advanced diagnostic tools and evidence-based treatment approaches.
What are Recent Medical Researches on Autoimmune Disease
Autoimmune disease research is a vast and active field, so highlighting all “recent” advancements is difficult. However, I can share some exciting areas of ongoing research with significant potential:
1. Microbiome Manipulation
Exploring the link between gut bacteria and autoimmune diseases. Studies investigate how altering the gut microbiome through diet, probiotics, or fecal transplants might influence disease activity.
2. Precision Medicine
Utilizing genetic and molecular profiling to tailor treatments to individual patients based on their specific disease characteristics and response to therapies. This personalized approach aims for more effective and targeted interventions.
3. Stem Cell Therapy
Investigating the potential of stem cells to repair damaged tissues in autoimmune diseases or to modulate the immune system for disease control.
4. Novel Immunotherapies
Developing next-generation drugs beyond traditional immunosuppressants. These new therapies aim to specifically target specific immune cells or pathways involved in autoimmune disease development.
5. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Utilizing AI algorithms to analyze vast datasets of patient information and identify patterns for improved diagnosis, predicting disease progression, and selecting personalized treatment plans.
6. Environmental Triggers
Investigating the role of environmental factors like exposure to chemicals, pollutants, or viruses in triggering or exacerbating autoimmune diseases. Understanding these triggers could lead to preventive strategies.
Key Facts about Autoimmune Disease (AID)
We have added few of important facts and information about AID below-
| Key Facts about Auto Immune Diseases | |
| Fact | Description |
| Origin | Mid-20th century. |
| Discovered | 1938 |
| By whom? | William Dameshek and Steven Schwartz |
| Definition | Group of conditions where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues. |
| Types | Over 80, including- Rheumatoid Arthritis, Lupus, Psoriasis, Celiac Disease, Type 1 Diabetes, Multiple Sclerosis, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Sjögren’s Syndrome, Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis, Graves’ Disease |
| Symptoms | Vary depending on the type but can include: Fatigue, Pain, Inflammation, Skin problems, Digestive issues, Neurological problems |
| Causes | Unknown, likely involve complex interactions between: Genetic predisposition, Environmental triggers (Viruses, toxins, chemicals), Gut health imbalances |
| Diagnosis | Based on a combination of factors: Clinical presentation (Symptoms, medical history), Blood tests (Autoantibody tests, inflammatory markers), Imaging tests (X-rays, MRIs, ultrasounds), Biopsies (In some cases) |
| Treatment | Focuses on managing symptoms and preventing flares, involving: Medications (Immunosuppressants, biologics, pain relievers), Physical therapy (Improve joint function, manage pain), Lifestyle changes (Diet, exercise, stress management). |
| Risk Factors | Can include: Family history of AID, Age (Onset more frequent in young to middle adulthood), Sex (Women more affected than men for some types), Smoking, Gut microbiome imbalances. |
| Medical Terminologies | Key terms to understand AID: Autoantibodies (Mistakenly target own tissues), Autoimmunity (Immune system attacks self), Antigen-presenting cells (Activate immune response), Cytokine storm (Excessive immune system activation), T cells and B cells (Specific immune cell types involved) |
| Cure | Currently no cure exists, but research aims to: Prevent disease development, Slow disease progression, Stop disease activity. |
| Common Treatment | Varies by type, but often includes: Medications tailored to specific AID, Lifestyle modifications based on individual needs, Physical therapy for affected joints and muscles. |
| Mortality Rate | Differs among AID types, with some having higher mortality than others. |
| Public Impact | Over 200 million people globally live with AID, impacting: Healthcare costs, Lost productivity, Quality of life. |
| Prevention Tips | While not guaranteed, promoting a healthy lifestyle may offer some protection for certain types, including: Balanced diet (Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains), Regular exercise (Moderate physical activity most days), Stress management (Techniques like yoga or meditation), Maintaining healthy weight, Getting enough sleep, Quitting smoking, Consulting a healthcare professional for personalized advice. |
FAQs on Autoimmune Disease – UPSC Questions on Autoimmune Disease
Question-1: What are Autoimmune Diseases (AIDs)?
Answer. AIDs are a diverse group of chronic illnesses where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, causing various symptoms and organ damage.
Question-2: How many people are affected by AIDs?
Answer. Globally, over 200 million people live with AIDs, making it a significant public health concern.
Question-3: What are some common types of AIDs?
Answer. Examples include rheumatoid arthritis (RA), lupus, type 1 diabetes, celiac disease, and multiple sclerosis (MS).
Question-4: What are the main causes of AIDs?
Answer. The exact cause is unknown, but likely involves complex interactions between genetic predisposition and environmental factors like infections or toxins.
Question-5: What are the key symptoms of AIDs?
Answer. Symptoms vary depending on the type of AID but can include fatigue, pain, inflammation, skin problems, digestive issues, and neurological problems.
Question-6: How are AIDs diagnosed?
Answer. Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes biopsies.
Question-7: What are the current treatment options for AIDs?
Answer. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing flares, using medications (immunosuppressants, biologics), physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Question-8: Are there any potential cures for AIDs?
Answer. Currently, no cure exists, but ongoing research aims to develop treatments that prevent, slow, or stop disease progression.
Question-9: What are the main economic and social impacts of AIDs?
Answer. AIDs cause significant healthcare costs, lost productivity, and reduced quality of life for individuals and societies.
Question-10: What are some initiatives being taken to address the challenge of AIDs?
Answer. Increased research funding, public awareness campaigns, and support groups are playing important roles in tackling this global health challenge.
Bonus FAQ
Question-11: What are some UPSC-relevant aspects of AIDs?
Answer. These are some UPSC-relevant Aspects of AIDs-
- Public health policy: understanding the burden of AIDs and exploring policy measures for improved diagnosis, treatment, and support.
- Social welfare schemes: recognizing the need for social security and economic support for individuals affected by AIDs.
- Science and technology: appreciating the role of research advancements in finding new diagnostic tools, treatments, and potential cures for AIDs.




Hello there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my old room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!